GDAL Image Formats¶
GeoServer can leverage the ImageI/O-Ext GDAL libraries to read selected coverage formats. GDAL is able to read many formats, but for the moment GeoServer supports only a few general interest formats and those that can be legally redistributed and operated in an open source server.
The following image formats can be read by GeoServer using GDAL:
- DTED, Military Elevation Data (.dt0, .dt1, .dt2): http://www.gdal.org/frmt_dted.html
- EHdr, ESRI .hdr Labelled: <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_various.html#EHdr>
- ENVI, ENVI .hdr Labelled Raster: <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_various.html#ENVI>
- HFA, Erdas Imagine (.img): <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_hfa.html>
- JP2MrSID, JPEG2000 (.jp2, .j2k): <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_jp2mrsid.html>
- MrSID, Multi-resolution Seamless Image Database: <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_mrsid.html>
- NITF: <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_nitf.html>
- ECW, ERDAS Compressed Wavelets (.ecw): <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_ecw.html>
- JP2ECW, JPEG2000 (.jp2, .j2k): http://www.gdal.org/frmt_jp2ecw.html
- AIG, Arc/Info Binary Grid: <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_various.html#AIG>
- JP2KAK, JPEG2000 (.jp2, .j2k): <http://www.gdal.org/frmt_jp2kak.html>
Installing GDAL extension¶
From GeoServer version 2.2.x, GDAL must be installed as an extension. To install it:
Navigate to the GeoServer download page
Find the page that matches the version of the running GeoServer.
Warning
Be sure to match the version of the extension with that of GeoServer, otherwise errors will occur.
Download the GDAL extension. The download link for GDAL will be in the Extensions section under Coverage Format.
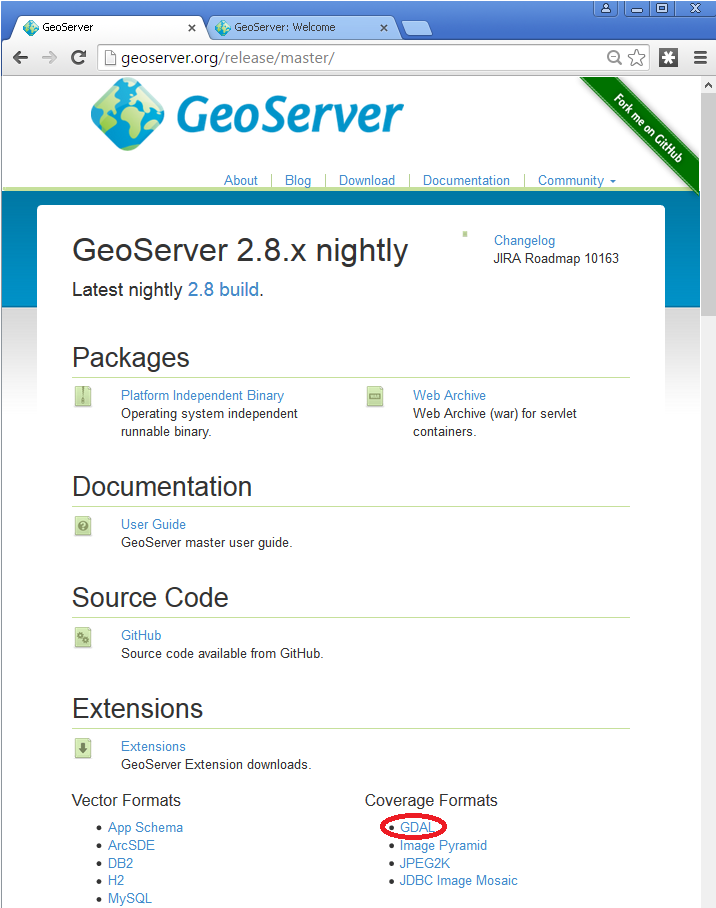
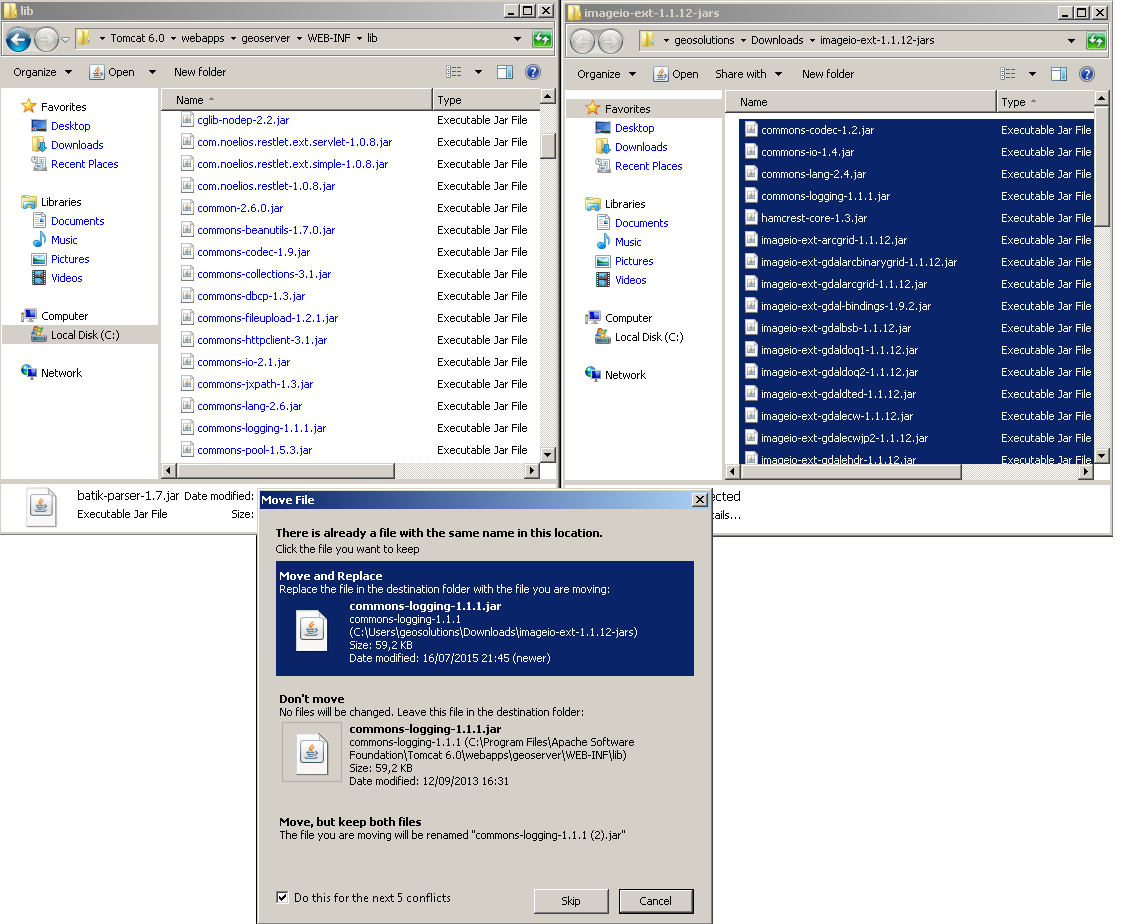
- Extract the files in this archive to the
WEB-INF/libdirectory of your GeoServer installation. On Windows You may be prompted for confirmation to overwrite existing files, confirm the replacement of the files
Moreover, in order for GeoServer to leverage these libraries, the GDAL (binary) libraries must be installed through your host system’s OS. Once they are installed, GeoServer will be able to recognize GDAL data types. See below for more information.
Installing GDAL native libraries¶
The ImageIO-Ext GDAL plugin for geoserver master uses ImageIO-Ext 1.1.12 whose artifacts can be downloaded from here.
Browse to the native and then gdal directory for the Image IO-Ext download link. Now you should see a list of artifacts that can be downloaded. We need to download two things now:
- The CRS definitions
- The native libraries matching the target operating system (more details on picking the right one for your windows installation in the “Extra Steps for Windows Platforms” section)
Let’s now install the CRS definitions.
- Click on the “gdal_data.zip” to download the CRS definitions archive.
- Extract this archive on disk and place it in a proper directory on your system.
- Create a GDAL_DATA environment variable to the folder where you have extracted this file. Make also sure that this directory is reachable and readable by the application server process’s user.
We now have to install the native libraries.
Assuming you are using a 64 bits Ubuntu 11 Linux Operating System (for instance), click on the linux folder and then on “gdal192-Ubuntu11-gcc4.5.2-x86_64.tar.gz” to download the native libraries archive (Before doing this, make sure to read and agree with the ECWEULA if you intend to use ECW).
If you are using a Windows Operating System make sure to download the archive matching your Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributables and your architecture. For example on a 64 bit Windows with 2010 Redistributables, download the gdal-1.9.2-MSVC2010-x64.zip archive
Extract the archive on disk and place it in a proper directory on your system.
Warning
If you are on Windows, make sure that the GDAL DLL files are on your PATH. If you are on Linux, be sure to set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to refer to the folder where the SOs are extracted.
Note
The native libraries contains the GDAL gdalinfo utility which can be used to test whether or not the libs are corrupted. This can be done by browsing to the directory where the libs have been extracted and performing a gdalinfo command with the formats options that shows all the formats supported. The key element of GDAL support in GeoServer is represented by the JAVA bindings. To test the bindings, the package contains a Java version of the gdalinfo utility inside the “javainfo” folder (a .bat script for Windows and a .sh for Linux), it is very important to run it (again, with the formats options) to make sure that the Java bindings are working properly since that is what GeoServer use. An error message like Can’t load IA 32-bit .dll on a AMD 64-bit platform in the log files is a clear indication of the fact that you downloaded mixed version of the tools, please go through the installation process again and pick the appropriate ones. More details on troubleshooting in section Note on running GeoServer as a Service on Windows below
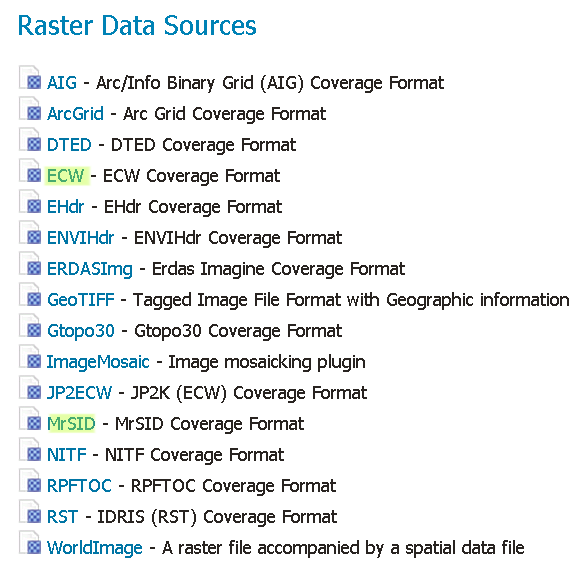
Once these steps have been completed, restart GeoServer. If all the steps have been performed correctly, new data formats will be in the Raster Data Sources list when creating a new data store in the Stores section as shown here below.
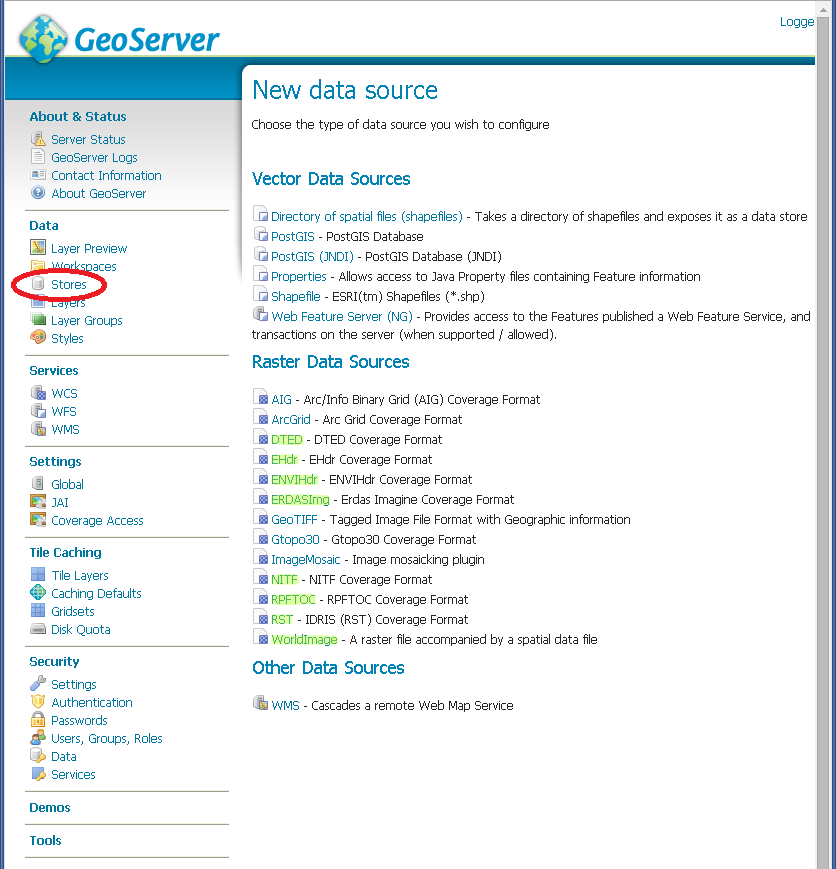
GDAL image formats in the list of raster data stores
if new formats don’t appear in the GUI and you see the following message in the log file:
it.geosolutions.imageio.gdalframework.GDALUtilities loadGDAL WARNING: Native library load failed.java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no gdaljni in java.library.path
that means that the installations failed for some reason.
Extra Steps for Windows Platforms¶
There are a few things to be careful with as well as some extra steps if you are deploying on Windows.
As stated above, we have multiple versions like MSVC2005, MSVC2008 and so on matching the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributables. Depending on the version of the underlying operating system you’ll have to pick up the right one. You can google around for the one you need. Also make sure you download the 32 bit version if you are using a 32 bit version of Windows or the 64 bit version (has a “-x64” suffix in the name of the zip file) if you are running a 64 bit version of Windows. Again, pick the one that matches your infrastructure.
Note on running GeoServer as a Service on Windows¶
Note that if you downloaded an installed GeoServer as a Windows service you installed the 32 bit version.
Simply deploying the GDAL ImageI/O-Ext native libraries in a location referred by the PATH environment variable (like, as an instance, the JDK/bin folder) doesn’t allow GeoServer to leverage on GDAL, when run as a service. As a result, during the service startup, GeoServer log reports this worrysome message:
it.geosolutions.imageio.gdalframework.GDALUtilities loadGDAL WARNING: Native library load failed.java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: no gdaljni in java.library.path
Taking a look at the wrapper.conf configuration file available inside the GeoServer installation (at bin/wrapper/wrapper.conf), there is this useful entry:
# Java Library Path (location of Wrapper.DLL or libwrapper.so) wrapper.java.library.path.1=bin/wrapper/lib
To allow the GDAL native DLLs getting loaded, you have 2 possible ways:
- Move the native DLLs on the referred path (bin/wrapper/lib)
- Add a wrapper.java.library.path.2=path/where/you/deployed/nativelibs entry just after the wrapper.java.library.path1=bin/wrapper/lib line.
Adding support for ECW and MrSID on Windows¶
If you are on Windows and you want to add support for ECW and MrSID there is an extra step to perform.
Download and install ECW and MrSID from here
In the Windows packaging ECW and MrSID are built as plugins hence they are not loaded by default but we need to place their DLLs in a location that is pointed by the GDAL_DRIVER_PATH environment variable. By default the installer place the plugins in C:\Program Files\GDAL\gdalplugins.
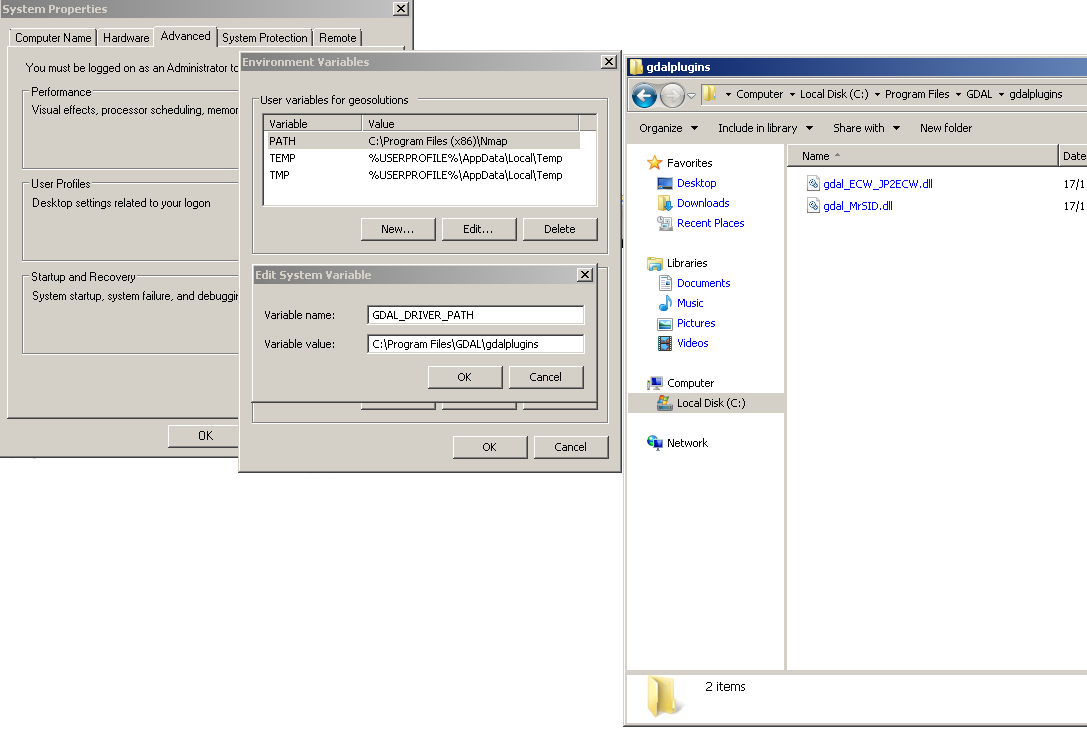
GDAL uses internally this env variable to look up additional drivers (notice that there are a few default places where GDAL will look anyway). For additional information, please see the GDAL wiki.
Restart GeoServer, you should now see the new data sources available
Configuring a DTED data store¶
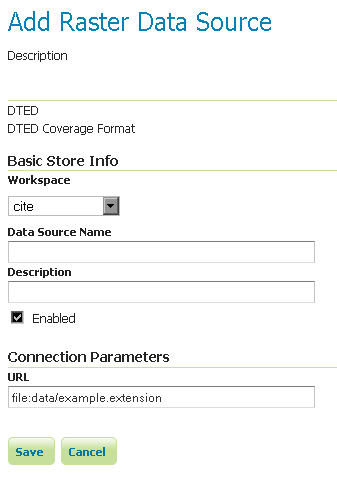
Configuring a DTED data store
Configuring a EHdr data store¶
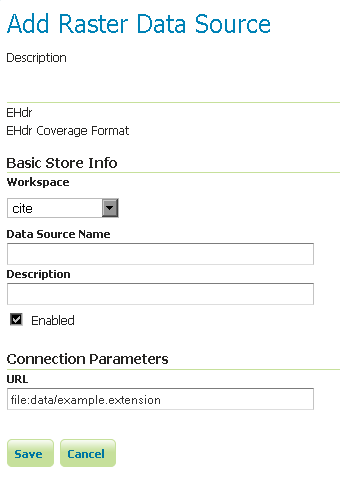
Configuring a EHdr data store
Configuring a ERDASImg data store¶
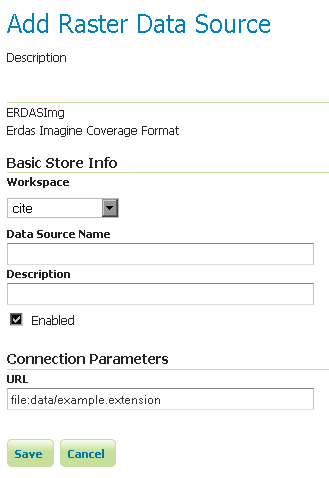
Configuring a ERDASImg data store
Configuring a JP2MrSID data store¶
Configuring a JP2MrSID data store
Configuring a NITF data store¶
Configuring a NITF data store